Above/featured: In San Francisco Bay on board Golden Gate Ferry westbound to Sausalito, the Golden Gate Bridge traverses over the deep narrow strait called Golden Gate, and connects San Francisco County (left) with Marin County (right). Photo, 18 Mar 2025 (X70).
It’s easy to mistake the association of the bright “international orange” colour of the Golden Gate Bridge with the Golden Gate. The name given to the deep narrow strip of water has much more to do with the Golden Horn in Istanbul. As part of his expeditions and geographic surveys in northern California in the mid-1840s, John Charles Frémont wrote the following for 27 April 1846 (Frémont 1848, pp. 31–33):
… The bay of San Francisco is separated from the sea by low mountain ranges. Looking from the peaks of the Sierra Nevada, the coast mountains present an apparently continuous line, with only a single gap, resembling a mountain pass. This is the entrance to the great bay, and is the only water communication from the coast to the interior country. Approaching from the sea, the coast presents a bold outline. On the south, the bordering mountains come down in a narrow ridge of broken hills, terminating in a precipitous point, against which the sea breaks heavily. On the northern side, the mountain presents a bold promontory, rising in a few miles to a height of two or three thousand feet. Between these points is the strait — about one mile broad, in the narrowest part, and five miles long from the sea to the bay. Passing through this gate,
* the bay opens to the right and left, extending in each direction about 35 miles, having a total length of more than 70, and a coast of about 275 miles. It is divided, by straits and projecting points, into three separate bays, of which the northern two are called San Pablo and Suisoon bays.
* Called Chrysopylae (Golden gate) on the map, on the same principle that the harbor of Byzantium (Constantinople afterwards) was called Chrysoceras (golden horn). The form of the harbor, and its advantages for commerce, (and that before it became an entrepot of eastern commerce,) suggested the name to the Greek founders of Byzantium. The form of the entrance into the bay of San Francisco, and its advantages for commerce, (Asiatic inclusive,) suggest the name which is given to this entrance.
Frémont’s description in 1848 is most likely the first documented mention, as San Francisco’s Chrysopylae (golden gate) reminded him of Constantinople’s Chrysoceras (golden horn). Today, the Greek noun has been dropped, and the world recognizes the narrow water entrance into San Francisco Bay simply as “Golden Gate”.
Around the Bay & City
Over a number of months in the Bay Area, I examined many lines of sight to the Golden Gate Bridge. My favourite has to be the Bay ferry between San Francisco and Sausalito.
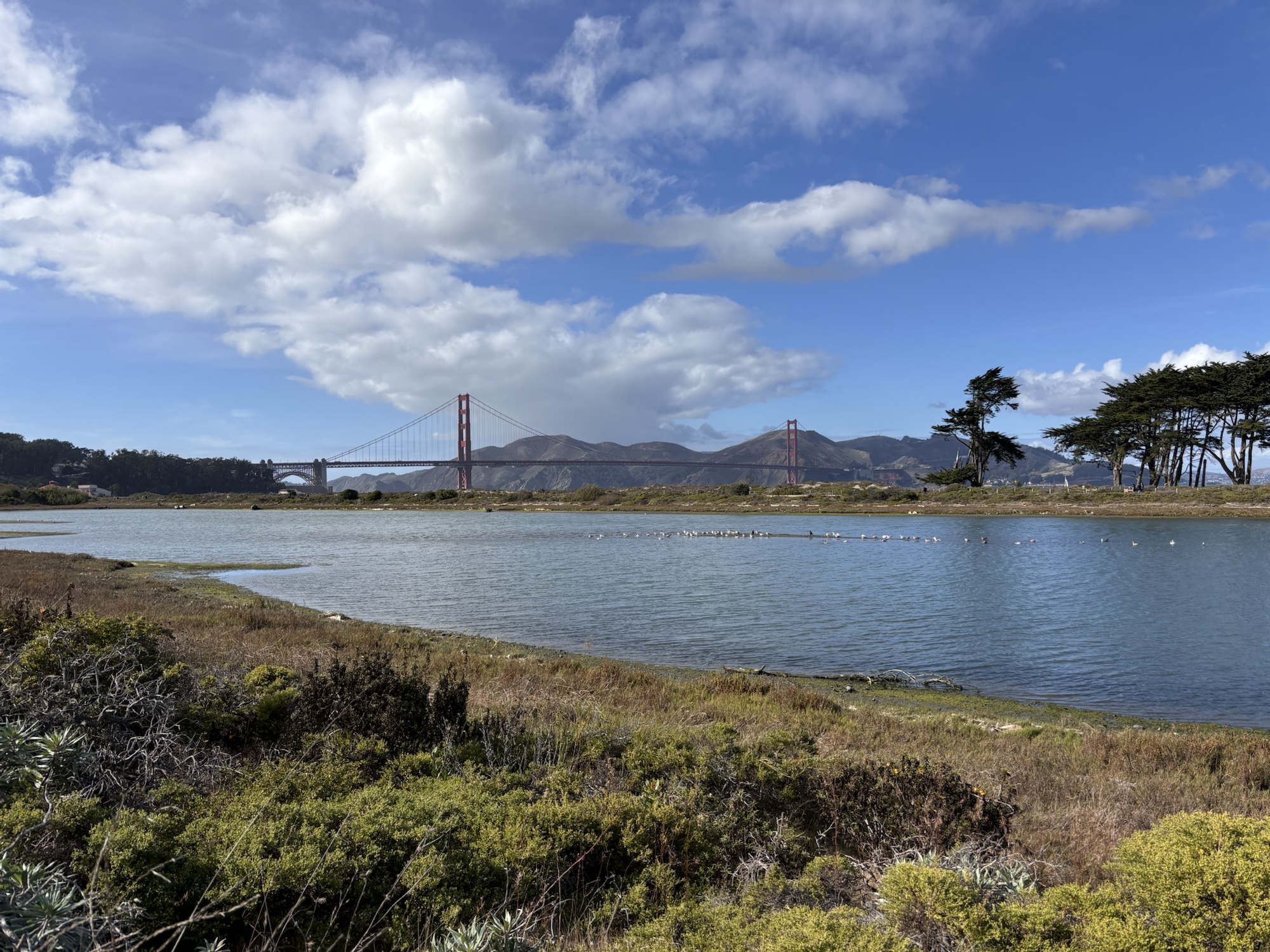

Crissy Field Marsh – 31 Oct 2024 (P15).

Fort Mason, next to the Great Meadow – 2 Dec 2024 (P15).

Lands End – 3 Dec 2024 (P15).

In morning light, facing west from Treasure Island – 6 Dec 2024 (P15).

Midday light at China Beach – 6 Dec 2024 (P15).

Dusk from the Golden Gate Bridge Welcome Center – 9 Dec 2024 (P15).

Torpedo Wharf – 26 Dec 2024 (P15).

San Francisco National Cemetery, facing northwest – 28 Dec 2024 (P15).
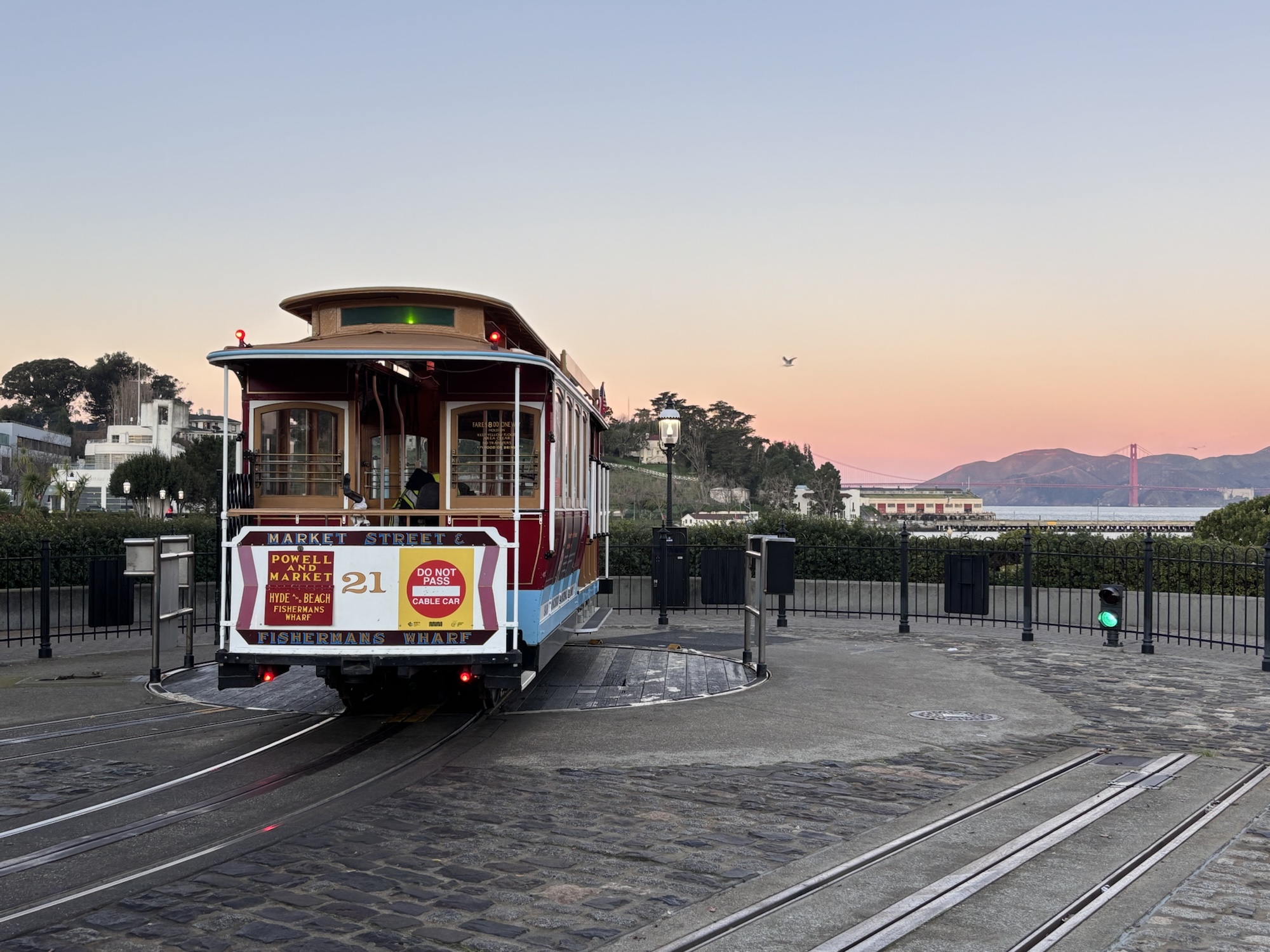

Powell-Hyde cable car turntable at dawn – 31 Dec 2024 (P15).

From the Coastal Trail, east to Lands End. Photo, 5 Jan 2025 (X70).
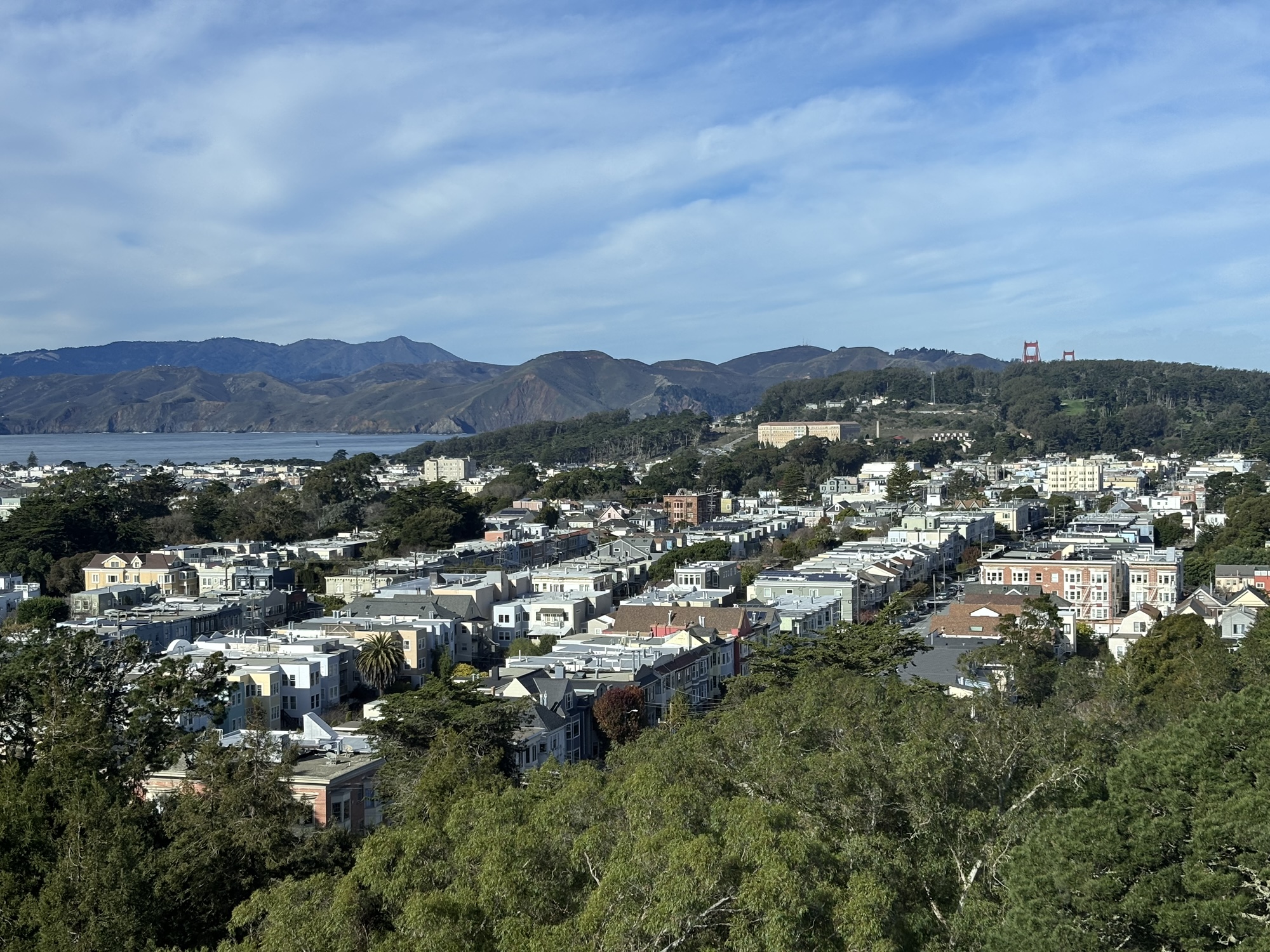

At upper right, the tops of the bridge towers appear over The Presidio, from de Young Museum’s Hamon Tower – 7 Jan 2025 (P15).
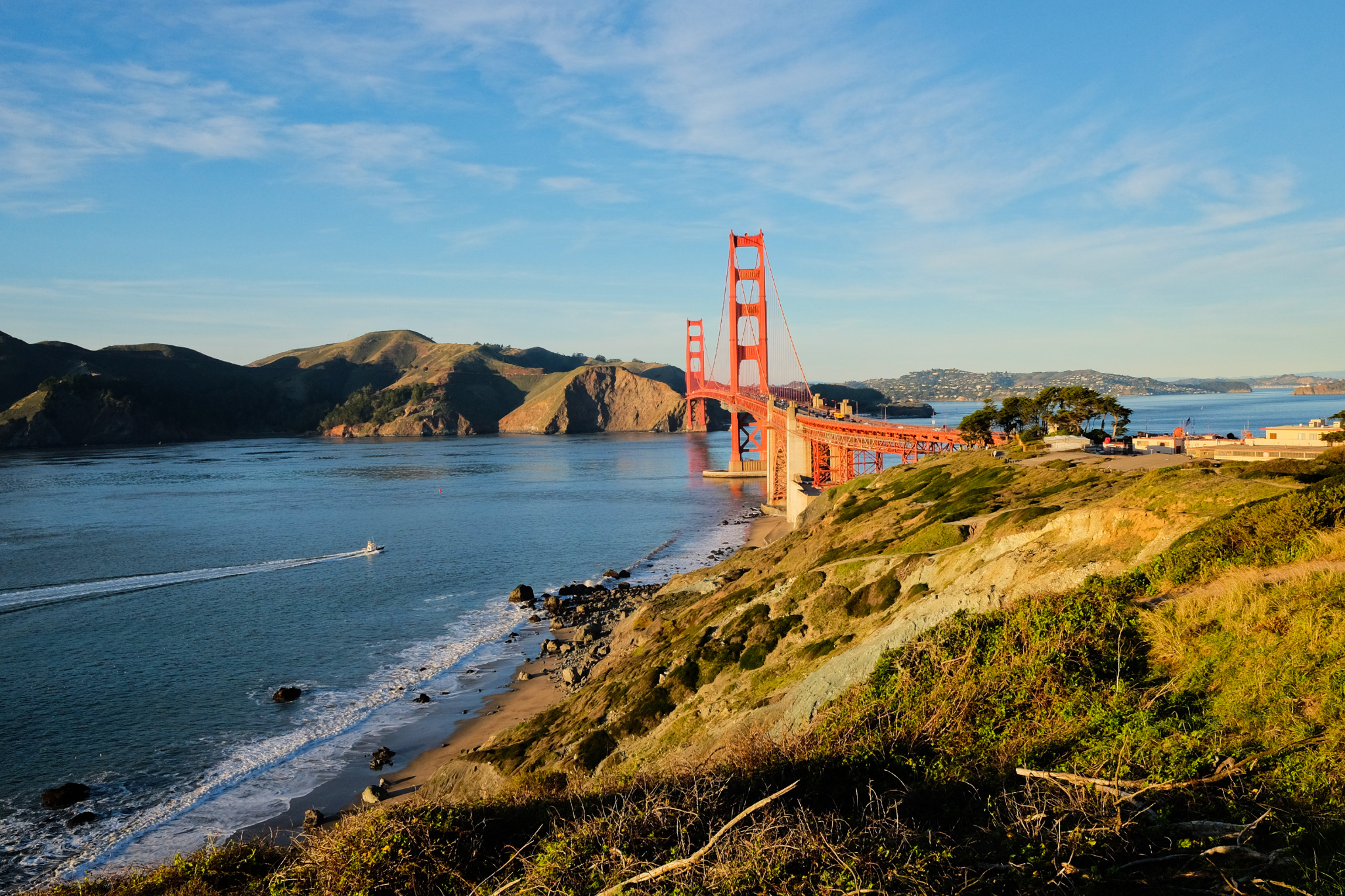

From Battery Godfrey in The Presidio. Access is from the Coastal Trail or the Golden Gate Bridge Visitor Center. Photo, 13 Jan 2025 (X70).

From Twin Peaks’ Christmas Tree Point, the Golden Gate bridge appears at top-centre; at right are St. Ignatius church and the University of San Francisco campus. Photo, 28 Jan 2025 (P15).

Marina Promenade – 5 Feb 2025 (P15).

Aquatic Cove: the bridge is almost fully covered in fog. Photo, 16 Feb 2025 (P15).
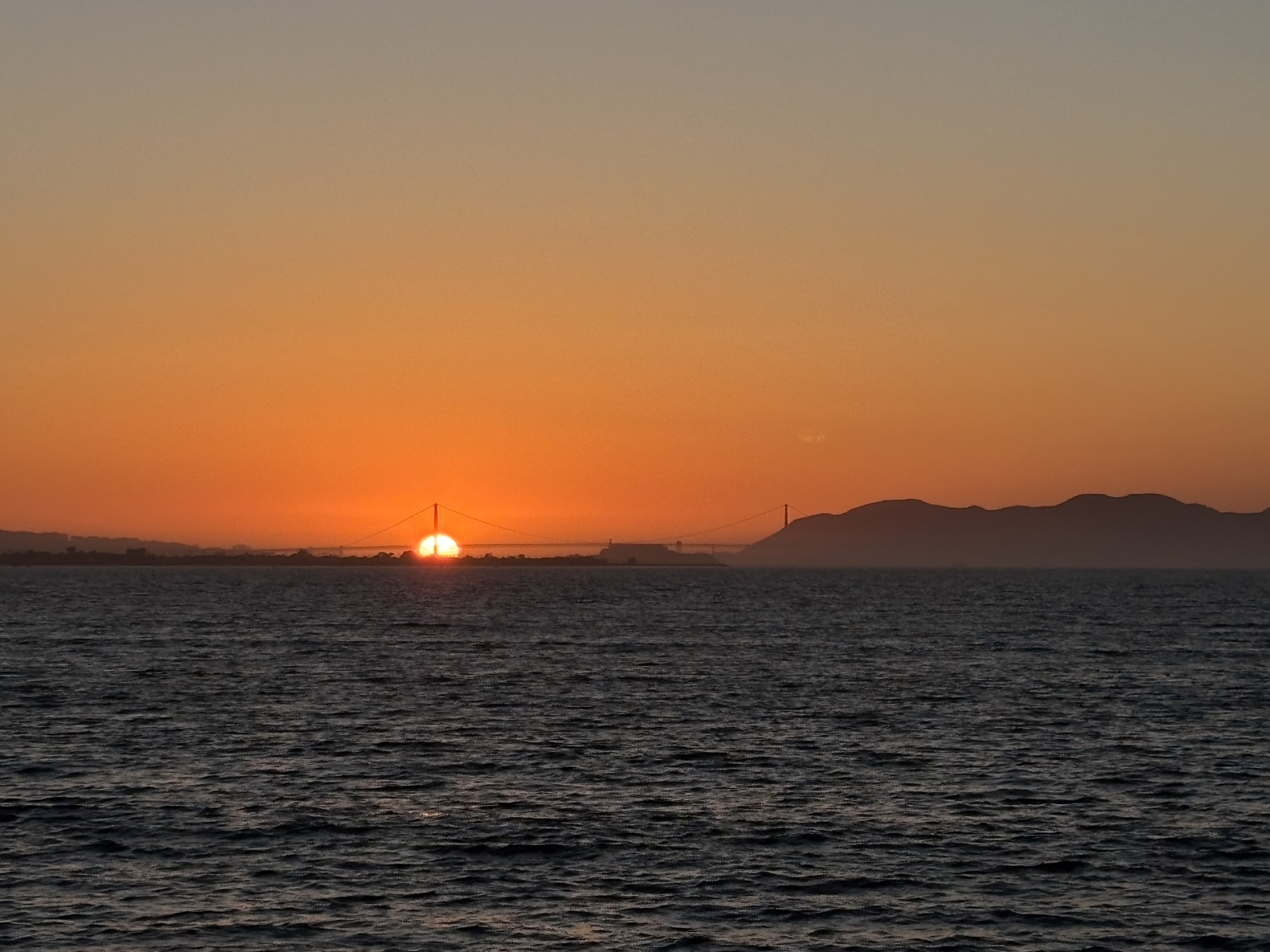

From Emeryville Marina Park: sunset intercepts one of the bridge’s towers – 25 Feb 2025 (P15).
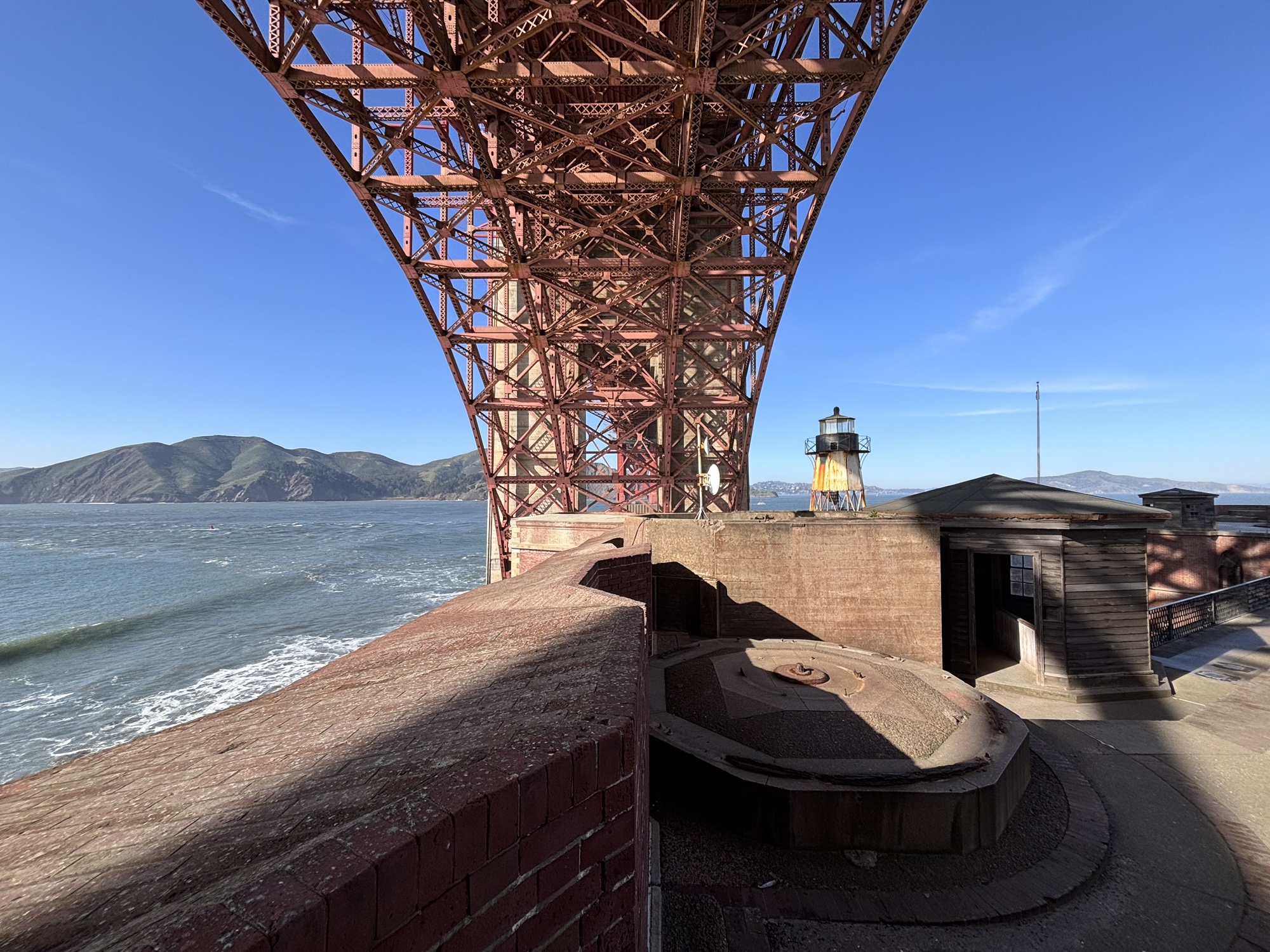

Underneath the bridge at Fort Point – 28 Feb 2025 (P15).
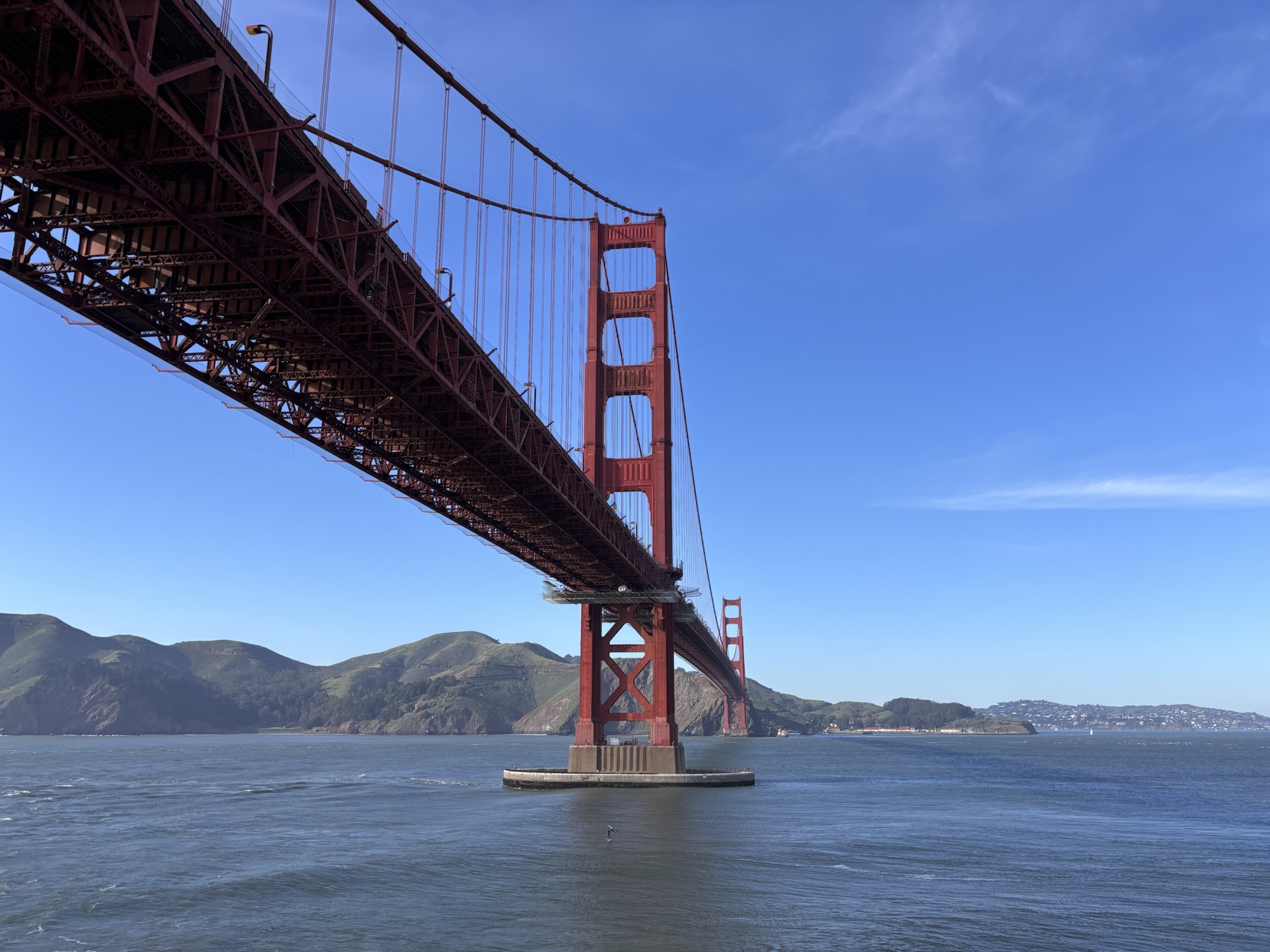

Next to the entrance for Fort Point and in front of Golden Gate strait – 28 Feb 2025 (P15).

Baker Beach – 11 Mar 2025 (P15).

In Richardson Bay, on Golden Gate Ferry westbound to Sausalito. The Sutro Tower also makes an appearance at left. Photo, 18 Mar 2025 (P15).

The Presidio, over Battery Marcus Miller – 26 Mar 2025 (P15).

From UCSF Parnassus Heights: at left-centre is The Landmark at Presidio (former military hospital), and at upper-right are the towers of the Golden Gate Bridge. Photo, 29 Mar 2025 (P15).

From the Tunnel Tops at the Presidio – 31 Mar 2025 (X70).
Sources
• Fremont, J.C., “Geographical memoir upon upper California, addressed to the Senate of the United States in 1848“, 30th United States Congress, no. 148 (Philadelphia: William McCarty, 1848). Digitized in 2015 by and online access at Internet Archive, via San Francisco Public Library: https://archive.org/stream/geographicalmemo00frmo_0/geographicalmemo00frmo_0_djvu.txt [last accessed May 2025].
• Fremont, J.C., “Map of Oregon and upper California from the surveys of John Charles Frémont and other authorities“, U.S. Library of Congress online: https://www.loc.gov/item/79692905/ [last accessed May 2025].
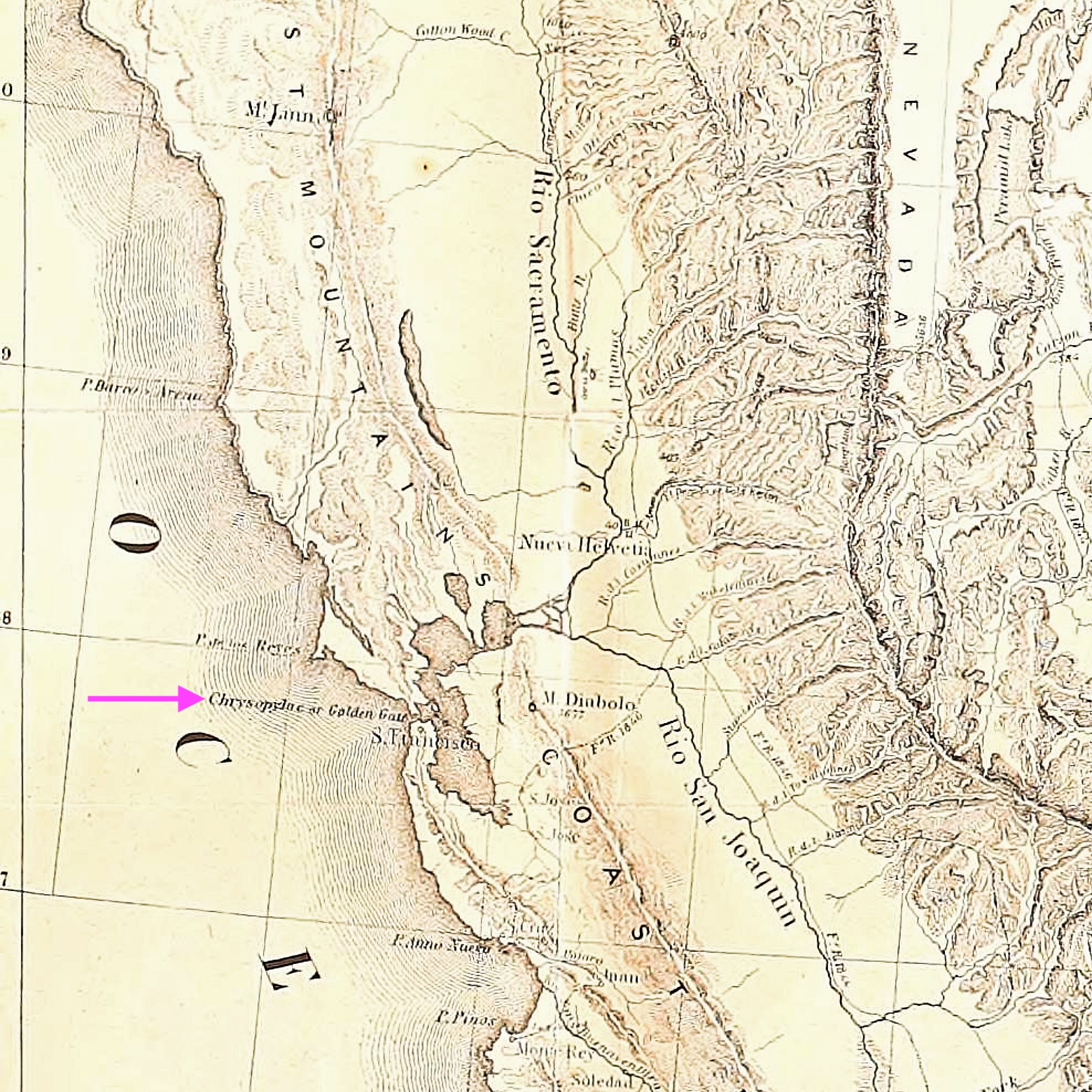
Section from Charles Preuss’ 1848 map included with John Charles Frémont’s 1848 memoir of his expeditions into Northern California. Reminding him of the Golden horn in Constantinople, Frémont named the narrow strait into San Francisco Bay as Chrysopylae or “Golden Gate”.
I made all photos above between 31 October 2024 and 31 March 2025 with a Fujifilm X70 fixed-lens prime (X70) and an iPhone15 (P15). I received neither request nor compensation for the content described here. This post appears on Fotoeins Fotografie at fotoeins DOT com as https://wp.me/p1BIdT-uS3.
37.774929
-122.419415


























